API Reference¶
This is intended for users of pyexcel.
Signature functions¶
Obtaining data from excel file¶
It is believed that once a Python developer could easily operate on list, dictionary and various mixture of both. This library provides four module level functions to help you obtain excel data in those formats. Please refer to “A list of module level functions”, the first three functions operates on any one sheet from an excel book and the fourth one returns all data in all sheets in an excel book.
get_array(**keywords) |
Obtain an array from an excel source |
get_dict([name_columns_by_row]) |
Obtain a dictionary from an excel source |
get_records([name_columns_by_row]) |
Obtain a list of records from an excel source |
get_book_dict(**keywords) |
Obtain a dictionary of two dimensional arrays |
In cases where the excel data needs custom manipulations, a pyexcel user got a
few choices: one is to use Sheet and Book,
the other is to look for more sophisticated ones:
- Pandas, for numerical analysis
- Do-it-yourself
get_book(**keywords) |
Get an instance of Book from an excel source |
get_sheet(**keywords) |
Get an instance of Sheet from an excel source |
The following two variants of the data access function use generator and should work well with big data files. However, you will need to call free_resources() to make sure file handles are closed.
iget_array(**keywords) |
Obtain a generator of an two dimensional array from an excel source |
iget_records([custom_headers]) |
Obtain a generator of a list of records from an excel source |
free_resources() |
Close file handles opened by signature functions that starts with ‘i’ |
Saving data to excel file¶
save_as(**keywords) |
Save a sheet from a data source to another one |
save_book_as(**keywords) |
Save a book from a data source to another one |
The following functions would work with big data and will work every well
with iget_array() and iget_records().
isave_as(**keywords) |
Save a sheet from a data source to another one with less memory |
isave_book_as(**keywords) |
Save a book from a data source to another one |
If you would only use these two functions to do format transcoding, you may enjoy a
speed boost using isave_as() and isave_book_as(),
because they use yield keyword and minimize memory footprint. However, you will
need to call free_resources() to make sure file handles are closed.
And save_as() and save_book_as() reads all data into
memory and will make all rows the same width.
Cookbook¶
merge_csv_to_a_book(filelist[, outfilename]) |
merge a list of csv files into a excel book |
merge_all_to_a_book(filelist[, outfilename]) |
merge a list of excel files into a excel book |
split_a_book(file_name[, outfilename]) |
Split a file into separate sheets |
extract_a_sheet_from_a_book(file_name, sheetname) |
Extract a sheet from a excel book |
Book¶
Here’s the entity relationship between Book, Sheet, Row and Column
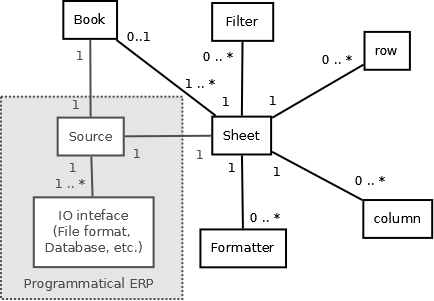
Attribute¶
Book.number_of_sheets() |
Return the number of sheets |
Book.sheet_names() |
Return all sheet names |
Conversions¶
Book.bookdict |
Get/Set data in/from bookdict format |
Book.url |
Set data in url format |
Book.csv |
Get/Set data in/from csv format |
Book.tsv |
Get/Set data in/from tsv format |
Book.csvz |
Get/Set data in/from csvz format |
Book.tsvz |
Get/Set data in/from tsvz format |
Book.xls |
Get/Set data in/from xls format |
Book.xlsm |
Get/Set data in/from xlsm format |
Book.xlsx |
Get/Set data in/from xlsx format |
Book.ods |
Get/Set data in/from ods format |
Book.stream |
Return a stream in which the content is properly encoded |
Save changes¶
Book.save_as(filename, **keywords) |
Save the content to a new file |
Book.save_to_memory(file_type[, stream]) |
Save the content to a memory stream |
Book.save_to_database(session, tables[, …]) |
Save data in sheets to database tables |
Book.save_to_django_models(models[, …]) |
Save to database table through django model |
Sheet¶
Constructor¶
Sheet([sheet, name, name_columns_by_row, …]) |
Two dimensional data container for filtering, formatting and iteration |
Attributes¶
Sheet.content |
Plain representation without headers |
Sheet.number_of_rows() |
The number of rows |
Sheet.number_of_columns() |
The number of columns |
Sheet.row_range() |
Utility function to get row range |
Sheet.column_range() |
Utility function to get column range |
Iteration¶
Sheet.rows() |
Returns a top to bottom row iterator |
Sheet.rrows() |
Returns a bottom to top row iterator |
Sheet.columns() |
Returns a left to right column iterator |
Sheet.rcolumns() |
Returns a right to left column iterator |
Sheet.enumerate() |
Iterate cell by cell from top to bottom and from left to right |
Sheet.reverse() |
Opposite to enumerate |
Sheet.vertical() |
Default iterator to go through each cell one by one from leftmost column to rightmost row and from top to bottom example. |
Sheet.rvertical() |
Default iterator to go through each cell one by one from rightmost column to leftmost row and from bottom to top example. |
Cell access¶
Sheet.cell_value(row, column[, new_value]) |
Random access to table cells |
Sheet.__getitem__(aset) |
By default, this class recognize from top to bottom from left to right |
Row access¶
Sheet.row_at(index) |
Gets the data at the specified row |
Sheet.set_row_at(row_index, data_array) |
Update a row data range |
Sheet.delete_rows(row_indices) |
Delete one or more rows |
Sheet.extend_rows(rows) |
Take ordereddict to extend named rows |
Column access¶
Sheet.column_at(index) |
Gets the data at the specified column |
Sheet.set_column_at(column_index, data_array) |
Updates a column data range |
Sheet.delete_columns(column_indices) |
Delete one or more columns |
Sheet.extend_columns(columns) |
Take ordereddict to extend named columns |
Data series¶
Any column as row name¶
Sheet.name_columns_by_row(row_index) |
Use the elements of a specified row to represent individual columns |
Sheet.rownames |
Return row names if any |
Sheet.named_column_at(name) |
Get a column by its name |
Sheet.set_named_column_at(name, column_array) |
Take the first row as column names |
Sheet.delete_named_column_at(name) |
Works only after you named columns by a row |
Any row as column name¶
Sheet.name_rows_by_column(column_index) |
Use the elements of a specified column to represent individual rows |
Sheet.colnames |
Return column names if any |
Sheet.named_row_at(name) |
Get a row by its name |
Sheet.set_named_row_at(name, row_array) |
Take the first column as row names |
Sheet.delete_named_row_at(name) |
Take the first column as row names |
Conversion¶
Sheet.array |
Get/Set data in/from array format |
Sheet.records |
Get/Set data in/from records format |
Sheet.dict |
Get/Set data in/from dict format |
Sheet.url |
Set data in url format |
Sheet.csv |
Get/Set data in/from csv format |
Sheet.tsv |
Get/Set data in/from tsv format |
Sheet.csvz |
Get/Set data in/from csvz format |
Sheet.tsvz |
Get/Set data in/from tsvz format |
Sheet.xls |
Get/Set data in/from xls format |
Sheet.xlsm |
Get/Set data in/from xlsm format |
Sheet.xlsx |
Get/Set data in/from xlsx format |
Sheet.ods |
Get/Set data in/from ods format |
Sheet.stream |
Return a stream in which the content is properly encoded |
Formatting¶
Sheet.format(formatter) |
Apply a formatting action for the whole sheet |
Filtering¶
Sheet.filter([column_indices, row_indices]) |
Apply the filter with immediate effect |
Transformation¶
Sheet.transpose() |
Rotate the data table by 90 degrees |
Sheet.map(custom_function) |
Execute a function across all cells of the sheet |
Sheet.region(topleft_corner, bottomright_corner) |
Get a rectangle shaped data out |
Sheet.cut(topleft_corner, bottomright_corner) |
Get a rectangle shaped data out and clear them in position |
Sheet.paste(topleft_corner[, rows, columns]) |
Paste a rectangle shaped data after a position |
Save changes¶
Sheet.save_as(filename, **keywords) |
Save the content to a named file |
Sheet.save_to_memory(file_type[, stream]) |
Save the content to memory |
Sheet.save_to_database(session, table[, …]) |
Save data in sheet to database table |
Sheet.save_to_django_model(model[, …]) |
Save to database table through django model |